This when you mix two liquids together and end up with a solid floating in the liquid. The solid is called a precipitate.
We did it when we made the chemical that they put on film. We got a white precipitate which we filtered out. We spread the white precipiate out on the filter paper and put it on the side in the sunshine with a coin over it.
Where the sun reached it, a reaction happened and the chemical went dark grey. Under the coin there was no light and no reaction so it stayed white.
Thursday, 18 December 2008
Covalent bonds
This is where atoms share electrons to make them think that they have full outside layers. They are weak bonds, so the chemicals have low melting and boiling points.
This is chlorine.
 An odd one is diamond. Each carbon atom is joined to 4 other atoms in a huge structure that is very strong.
An odd one is diamond. Each carbon atom is joined to 4 other atoms in a huge structure that is very strong.Ionic bonding
Atoms are only "happy" when their outside layers are either completely full or completely empty. The atom on the left had 2 atoms on its outside layer.
are only "happy" when their outside layers are either completely full or completely empty. The atom on the left had 2 atoms on its outside layer.
To get a completely empty layer, it loses two electrons. Taking away 2 negative electrons makes it doubly positive (2+).
The atom on the right had only 6 electrons on its outside layer. It needs 8 to have a full layer so it gains two electrons. Gaining 2 negative electrons makes it doubly negative (2-).
Opposites attract so the (2+) and the (2-) stay together. This is an ionic bond. The bonds are very strong so ionic compounds have very high melting and boiling points.

 are only "happy" when their outside layers are either completely full or completely empty. The atom on the left had 2 atoms on its outside layer.
are only "happy" when their outside layers are either completely full or completely empty. The atom on the left had 2 atoms on its outside layer. To get a completely empty layer, it loses two electrons. Taking away 2 negative electrons makes it doubly positive (2+).
The atom on the right had only 6 electrons on its outside layer. It needs 8 to have a full layer so it gains two electrons. Gaining 2 negative electrons makes it doubly negative (2-).
Opposites attract so the (2+) and the (2-) stay together. This is an ionic bond. The bonds are very strong so ionic compounds have very high melting and boiling points.

How to work out where to put electrons
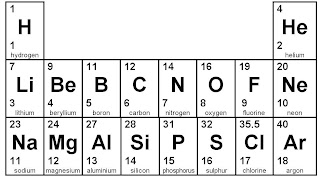
To work out where to put the electrons, start by looking at the Periodic Table. You need the bottom number to give you the number of electrons.
Let's start with ALUMINIUM. It has 13 electrons because the bottom number is 13.
We get the 13 like this:
- The first 2 go on the inside layer.
- The next 8 go on the second layer out.
- 2 and 8 make 10. That means there are 3 left for the outside layer.
Oxygen is the next example. It's bottom number on the Periodic Table is 8.
- 2 on the inside layer.
- That means that there are 6 left to go on the second layer. (It can have up to 8)
Final example is lithium. It's bottom number is 3.
- 2 on the inside layer.
- That leaves 1 on the second layer this time.
Tuesday, 16 December 2008
Electrolysis
Electolysis is where we use an electric current to split up an ionic compound that has been dissolved in water.
Our example was sodium chloride solution (salt water)
It contains H+ and OH- ions from the water.
It contains Na+ and Cl- ions from the chlorine.
Two Cl- ions lose 2 electrons at the positive electrode and turn into chlorine gas. It bleached blue litmus paper, turning it white.
The two electrons join up with two H+ ions at the negative electrode to make hydrogen gas.
Na+ and OH- are left behind. This makes sodium hydroxide which is an alkali and turns the universal indicator purple.
Our example was sodium chloride solution (salt water)
It contains H+ and OH- ions from the water.
It contains Na+ and Cl- ions from the chlorine.
Two Cl- ions lose 2 electrons at the positive electrode and turn into chlorine gas. It bleached blue litmus paper, turning it white.
The two electrons join up with two H+ ions at the negative electrode to make hydrogen gas.
Na+ and OH- are left behind. This makes sodium hydroxide which is an alkali and turns the universal indicator purple.
Tuesday, 10 June 2008
Re-sit papers
If you are re-sitting the year 10 modules on Monday 23 June, here's a link to get you the past papers that you need. There are mark schemes too.
http://www.aqa.org.uk/qual/gcse/newscience/extassessover.php
http://www.aqa.org.uk/qual/gcse/newscience/extassessover.php
Monday, 9 June 2008
Tuesday, 3 June 2008
Satellites
A geostationary orbit is one above the equator. It takes the satellite 24 hours to go round once. This means that satellite Y is always above town A. (Note that the satellite doesn't stay still. It does move but so does town A. They stay fixed relative to each other.)

Polar orbit goes over the poles and covers a lot of territory.

- Used for communications eg phone and TV
- Because the satellite is in a fixed position relative to the Earth so dishes can always point in the same direction.
- GPS satellites are geostationary too.
- You SatNav constantly checks where it is in relation to these satellites.

Polar orbit goes over the poles and covers a lot of territory.
- Many countries visited so good for spying.
- Close to the ground so better photos (GoogleEarth)
- Weather photos

Ultrasound
Think about what happens when light hits a window. Some of it goes through and some is reflected. You can choose to focus on what is reflected or on what is on the other side of the window. We call this partial reflection.
In the same way, ultrasound is partially reflected when it goes from one medium into another medium. The ultrasound changes speed when it goes from one medium to another. The bigger the change in speed, the more is reflected. It is the reflection that allows us to make up a picture using ultrasound scanning for eg foetuses.
There is a big change in speed between air and muscle, so if you fire ultrasound towards a woman's stomach, it would mostly reflect and not get into her. For this reason, they smear saline gel on first because there is less of a reflection between saline gel and muscle.
In the same way, ultrasound is partially reflected when it goes from one medium into another medium. The ultrasound changes speed when it goes from one medium to another. The bigger the change in speed, the more is reflected. It is the reflection that allows us to make up a picture using ultrasound scanning for eg foetuses.
There is a big change in speed between air and muscle, so if you fire ultrasound towards a woman's stomach, it would mostly reflect and not get into her. For this reason, they smear saline gel on first because there is less of a reflection between saline gel and muscle.
Friday, 23 May 2008
Ray diagrams for convex lenses
Reflection in a plane mirror
Concave mirrors
Let's make a concave mirror. We start off with a complete circle. It seems quite obvious at the moment that the middle of the circle is the centre of curvature.

Now let's mark out a section of the circle and then cut it out. You can see that it still has a centre of curvature even when it's just a cut section.

Now let's fire rays of light at it. Notice that they don't focus at the centre of curvature. That means that we also need to know about a second point - the focal point (or principal focus).

Now take a look at a proper ray diagram:

There are 3 possible rays you could draw, although only 2 appear on any diagram:
Ray 1: Horizontally from the tip of the object arrow to hit the mirror and bounce back through F.
Ray 2: Slants down straight through F to hit the mirror then bounces back horizontally.
Ray 3: Is a perfectly straight line going through the top of the image arrow and through point C.

Now let's mark out a section of the circle and then cut it out. You can see that it still has a centre of curvature even when it's just a cut section.


Now let's fire rays of light at it. Notice that they don't focus at the centre of curvature. That means that we also need to know about a second point - the focal point (or principal focus).

Now take a look at a proper ray diagram:
- It has C for centre of curvature and F for principal focus
- The curved lens has been drawn flat for the purposes of the diagram

There are 3 possible rays you could draw, although only 2 appear on any diagram:
Ray 1: Horizontally from the tip of the object arrow to hit the mirror and bounce back through F.
Ray 2: Slants down straight through F to hit the mirror then bounces back horizontally.
Ray 3: Is a perfectly straight line going through the top of the image arrow and through point C.
Real and virtual images
For the purposes of exam answers, this is what you have to say:
A real image can be projected onto a piece of paper.
A virtual image cannot be projected onto a piece of paper.
A real image can be projected onto a piece of paper.
- We did this is class to see an upside down picture of the room and to get pictures of the upside down triangle.
- You can spot it on a diagram because it is where solid rays cross.
A virtual image cannot be projected onto a piece of paper.
- You can spot it on a diagram because it is where dotted rays cross.
The National Grid

Click on the picture to get it to a bigger size.
On this diagram, A is a step up transformer at the power station.
- A step up transformer increases the voltage (potential difference).
- At the same time the current is reduced.
- Current is responsible for heating up wires and wasting energy.
- So reducing the current reduces the energy wasted by heat.
Near your house there is step down transformer C that decreases the voltage ( and increases the current). The reason is that the massive voltage could give a fatal electric shock.
The National Grid is the system of power stations and power lines. It means that each town no longer has to have its own power station. Clearly there are economies of scale.
PS B is an intermediate step down transformer. There's one for every town that reduces the voltage from 400,000V to 33,000V before it is sent to the local substations to be reduced to 230V for your house.
Tuesday, 20 May 2008
Elliptical orbits

The orbit of the Earth around the Sun is not a perfect circle. It is slightly oval. We say that it is an ellipse. Therefore the orbit is elliptical.
The Sun is not in the centre. It is slightly to one side at a point called the FOCUS.
All of the planets follow elliptical orbits.
On the mock exam there was a question about an object going around the Sun. Should scientists vote on whether or not it should be a planet? The answer was to wait for more evidence to decide whether it might be something else like a COMET. Note: moons don't directly orbit the Sun: they orbit planets. The orbits of comets are particularly elliptical.
Friday, 16 May 2008
Electromagnetic induction
The syllabus has certain crucial points they keep going over:
- Electromagnetic induction occurs when eg a coil cuts the magnetic field of a spinning magnet.
- You have to say that a potential difference (voltage) is induced.
- THEN the potential difference causes a current to flow.
Supernova
When a large star reaches the end of its life, there is a massive explosion called a supernova.
Stars normally make new elements by the process called NUCLEAR FUSION.
This involves heat and pressure making positive nuclei stick together to make larger elements. Positive nuclei normally repel each other.
In stars like the Sun, the temperatures are only enough to turn hydrogen into helium.
However, the heat and pressure in a supernova are so huge that nuclear fusion can make ALL of the elements that exist.
Hence all the atoms in your body were made in a supernova billions of years ago. FACT!
Stars normally make new elements by the process called NUCLEAR FUSION.
This involves heat and pressure making positive nuclei stick together to make larger elements. Positive nuclei normally repel each other.
In stars like the Sun, the temperatures are only enough to turn hydrogen into helium.
However, the heat and pressure in a supernova are so huge that nuclear fusion can make ALL of the elements that exist.
Hence all the atoms in your body were made in a supernova billions of years ago. FACT!
Transformers
The whole thing together is called a COIL. The individual parts are called TURNS.
You will only get a mark if you write like this:
"It is a step down transformer because there are more TURNS on the primary than on the secondary."
You will only get a mark if you write like this:
"It is a step down transformer because there are more TURNS on the primary than on the secondary."
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)






